The Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) is an evolution of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) designed to provide faster convergence in Ethernet networks. RSTP achieves rapid convergence by introducing several improvements over STP.
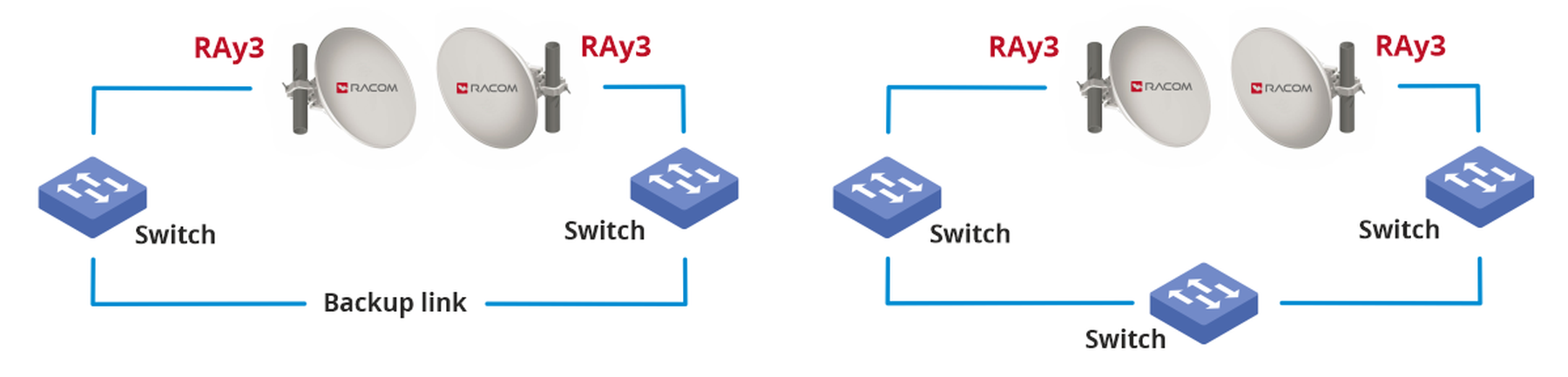
This combination can be used, for example, with a parallel backup link or in a circular topology as shown in the figures:
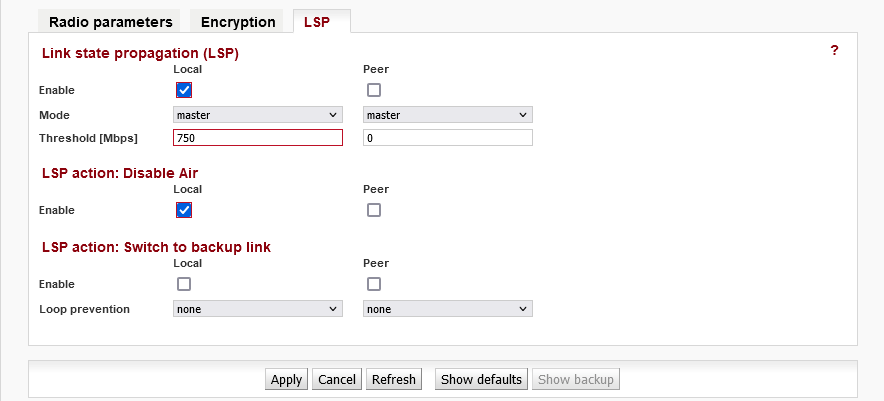
To configure according to these schemes, it is sufficient to enable the LSP function on one side of the link and select “Disable Air” as the action. In this case, when the Tx speed on the local unit drops below 750 Mbps (it can be changed at will), the connection of the ETH1 and ETH2 ports to the port AIR is interrupted. Data will no longer pass through the link and the RSTP protocol will recognise that this link is down and stop using it.
| Note | |
|---|---|
The RSTP function must be set accordingly on the switches in the network. |
| Note | |
|---|---|
RAy links are transparent to RSTP packets. |