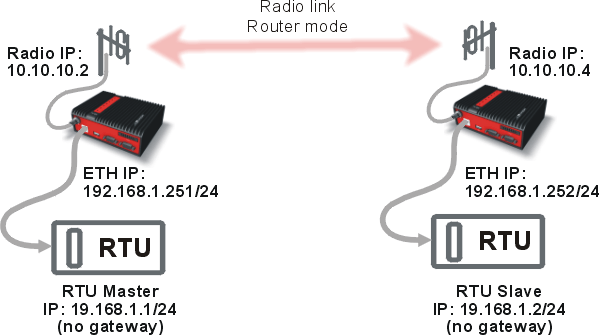
Even though RipEX works as a standard IP router, RipEX can interconnect equal IP subnets behind different RipEX units without defining default gateways. It can be done with the ARP proxy feature.
| Note | |
|---|---|
See the RipEX manual, Chapter 2.3 Router mode for configuration examples without ARP proxy usage. |
RipEX can reply to any ARP request to mimic it has this particular IP address (RipEX can reply to more ARP requests). This feature is typically used when RTU’s IP addresses behind different RipEX units are within the same IP subnet and the RTUs do not provide routing capabilities.
In this diagram RTUs do not have routing capabilities (i.e. RTU expects its counterpart is within the same physical Ethernet LAN). If the RTU Master starts to communicate with RTU Slave, it requests the RTU Slave’s MAC address. The RTU Slave is a member of the same physical LAN so the RTU Slave does not reply. However, when RipEX (radio IP 10.10.10.2) has ARP proxy enabled, it replies to this ARP request.
So with the ARP proxy functionality, local RipEX can mimic any IP address and reply to ARP requests. In our case, the RTU Master would consider the RipEX MAC address as the Slave MAC address. And with the appropriate routing rules in RipEX units, we can achieve the needed interconnectivity. We do not need to set anything on the connected RTUs – no gateway, no routing rules.
| Important | |
|---|---|
Be very careful when using this feature, ARP proxy can disable all the traffic on the LAN! |
| Note | |
|---|---|
|