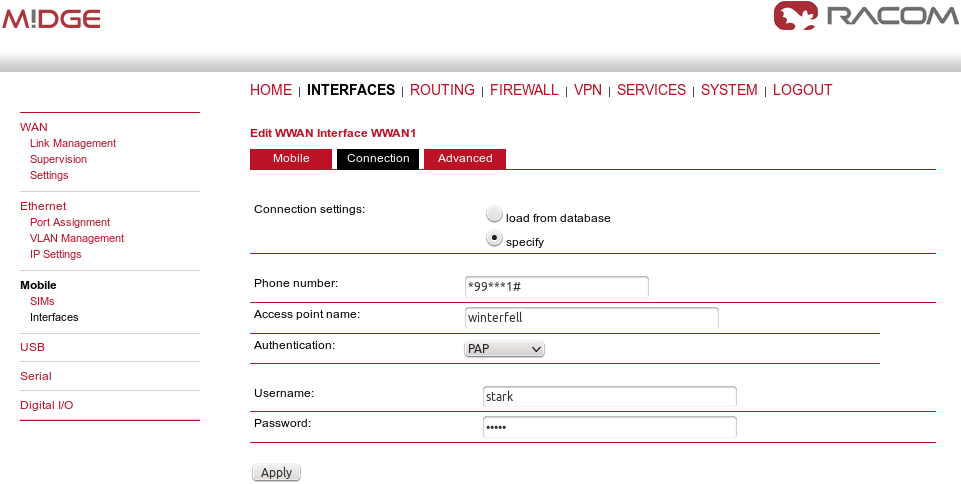
In the INTERFACES – Mobile – Interfaces menu, configure the private APN as defined by your service provider.
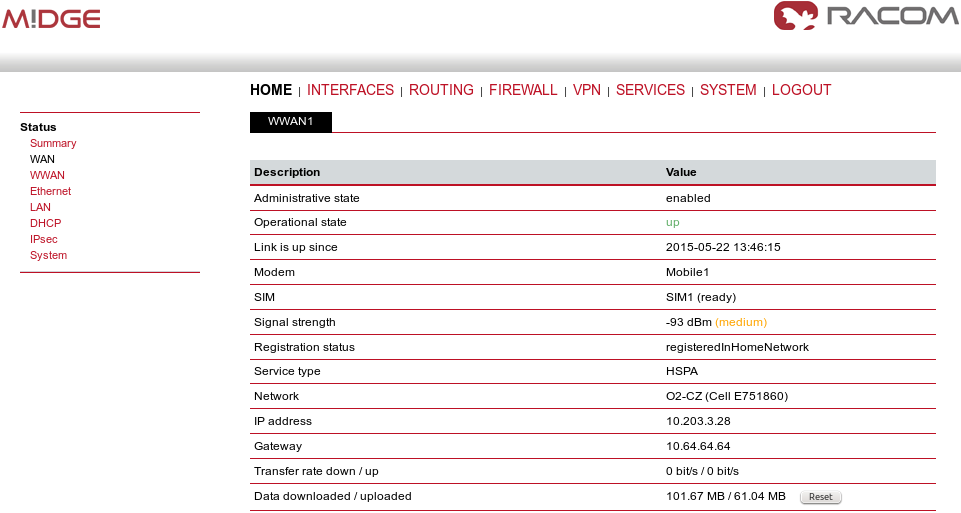
Once established, you can check the connection status in the HOME menu.
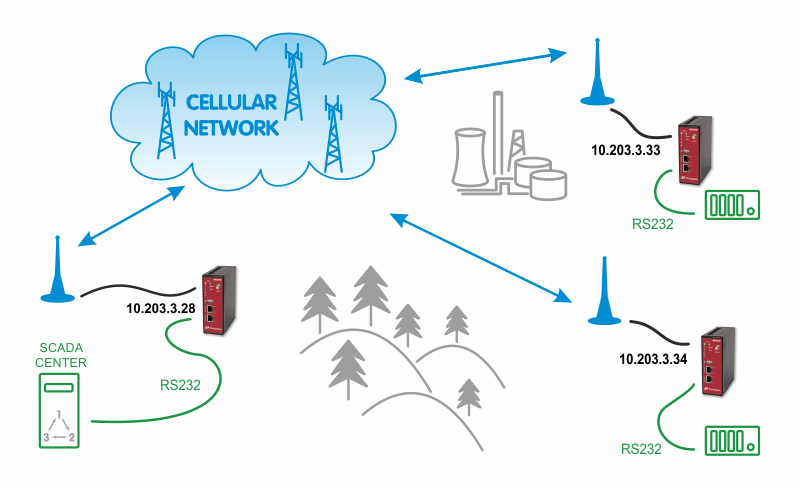
Configure other units with the appropriate credentials. In our example the Master M!DGE obtained the IP address 10.203.3.28 and the remote M!DGE units have 10.203.3.33 and 10.203.3.34.
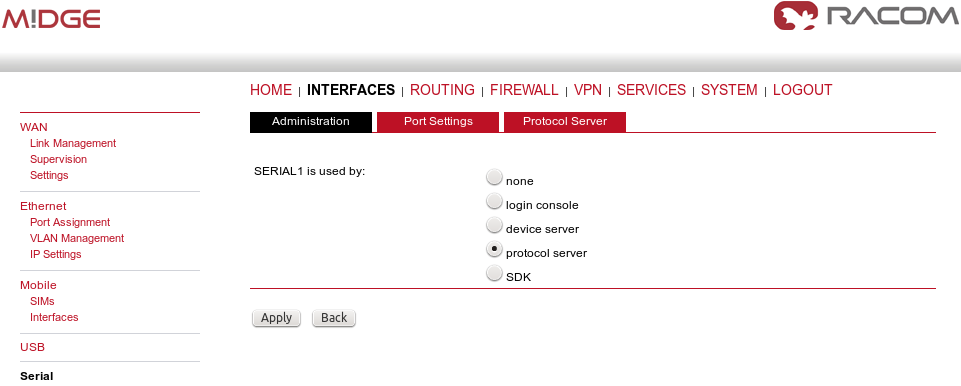
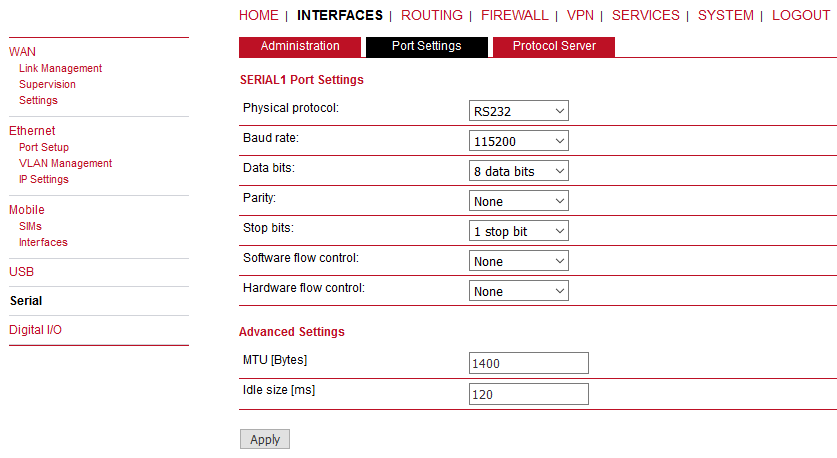
Our example will explain the Modbus Master-slave configuration with two slave units. On the Master station, select the INTERFACES – Serial menu and set the Protocol server option.
Configure the correct RS232 parameters such as baud rate, stop bits, …
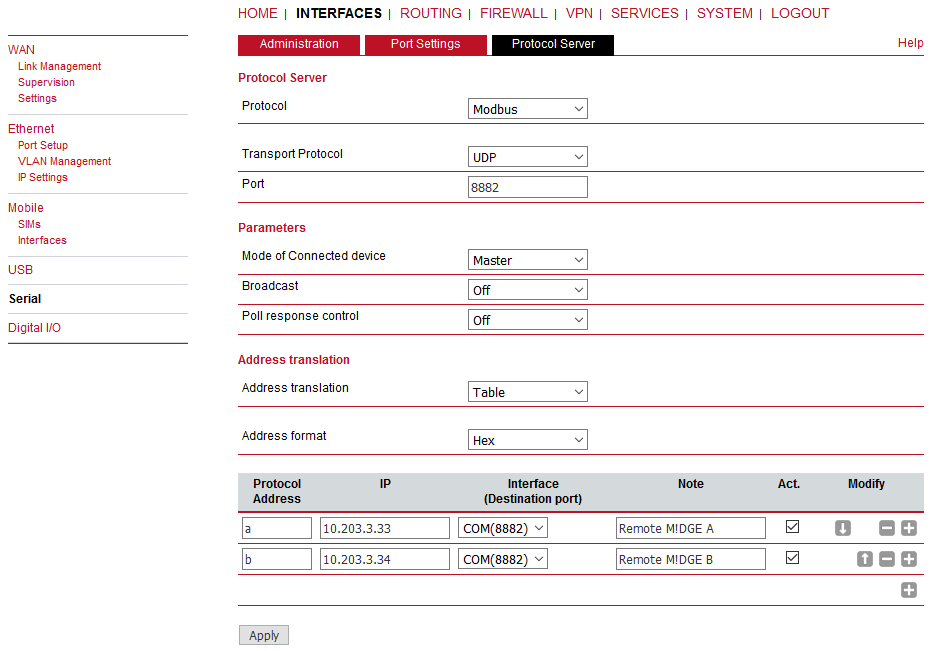
Set the MTU to default 1400 Bytes and Idle to 120 ms. See the manual for details. Go to the Protocol server menu and configure the Master parameters. Focus on the correct Address translation. You can either use mask or table for this purpose. If in doubts, open the Help window via the button located on top right corner. This Help explains the whole Protocol server functionality.
In the example below, the Master translates addresses A and B (hex) into IP addresses (and vice versa) 10.203.3.33, resp. 10.203.3.34. Using the port 8882 is mandatory if the remote device is connected via M!DGE RS232 interface.
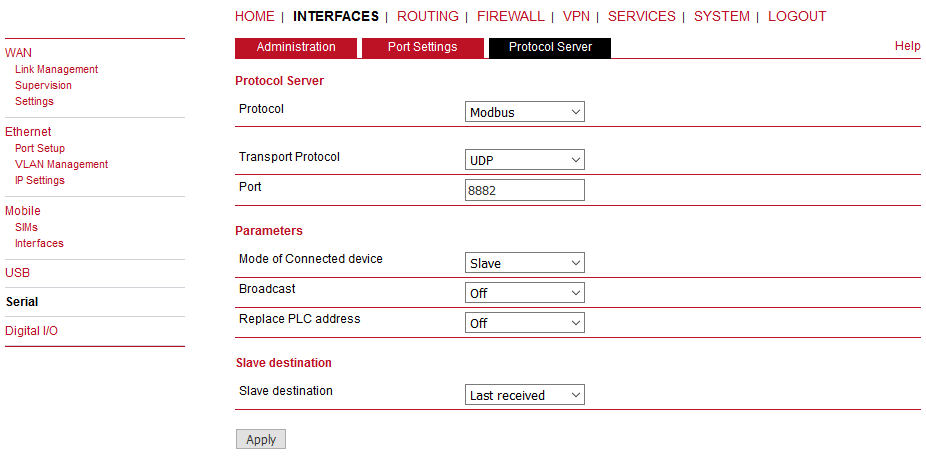
The Slave configuration is very straightforward. You set the Modbus Mode to “slave” and Slave destination to “Last received”.
| Important | |
|---|---|
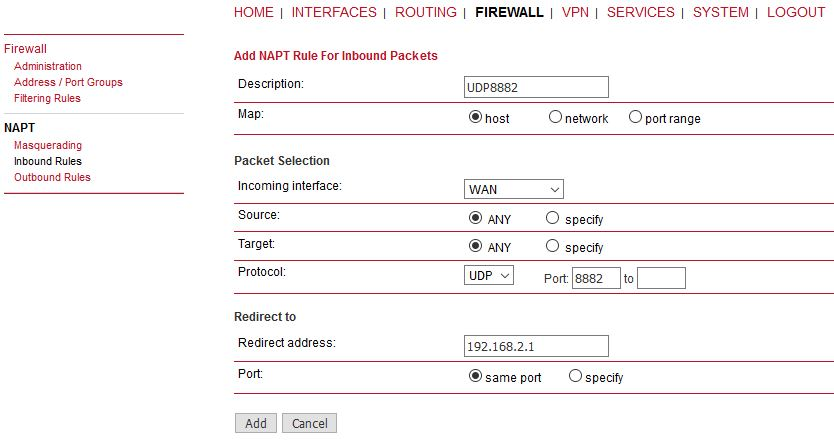
“Protocol server” daemon listens only on LAN1 IP address. This is fixed and cannot be changed currently (FW 4.4.40.101 and older). Port Forwarding is required to be set in M!DGE units in a way that received data are forwarded to LAN1 IP on UDP port 8882. Received interface can be the WWAN IP, OpenVPN TUN interface etc. |
In case that you encounter any issue, you can read the Protocol Server Help which is reachable from the
right top corner of the page. Sending the issue description to our
technical support at
<support@racom.eu> is possible. Please
try to include the following information:
The issue description (together with topology, required technology, …)
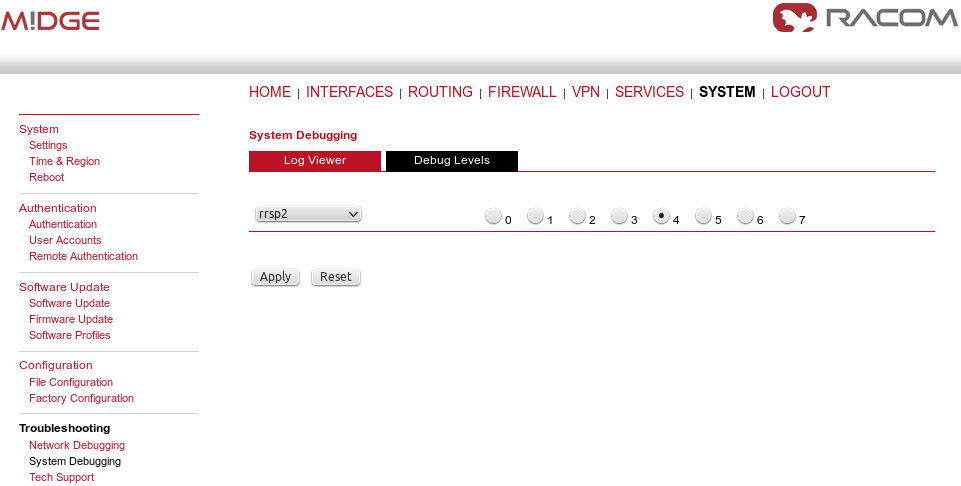
Please increase the debug level of rrsp2 daemon first (SYSTEM – Troubleshooting – System Debugging – Debug Levels – set rrsp2 to “4”). When applied, try to run your application and then download the Tech Support package (can be downloaded from the SYSTEM – Troubleshooting – Tech Support menu).
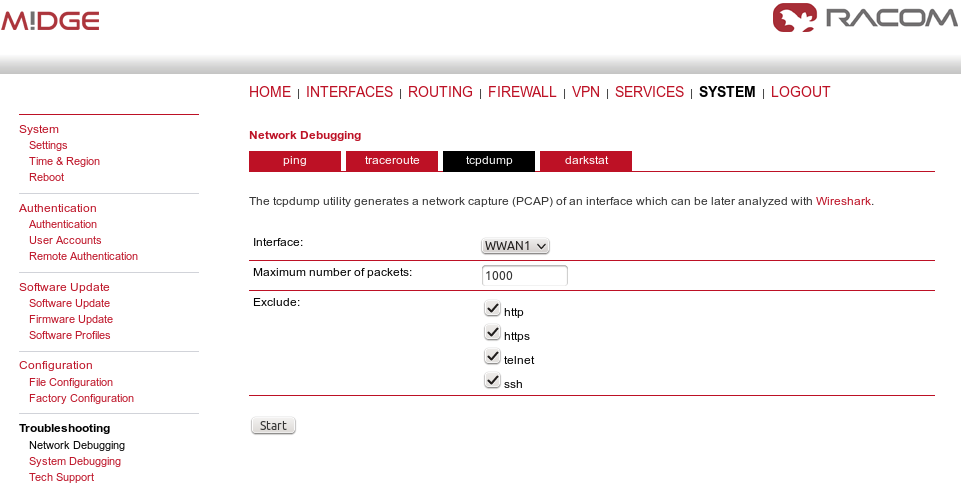
You can also include the WWAN interface monitoring output: SYSTEM – Troubleshooting – Network debugging – tcpdump – Set interface to “wwan1” and check all the “Exclude” boxes. Click start, run your application and after a while, stop the tcpdump again and download the file.
| Note | |
|---|---|
It is not possible to monitor the serial interface in M!DGE/MG102i. |