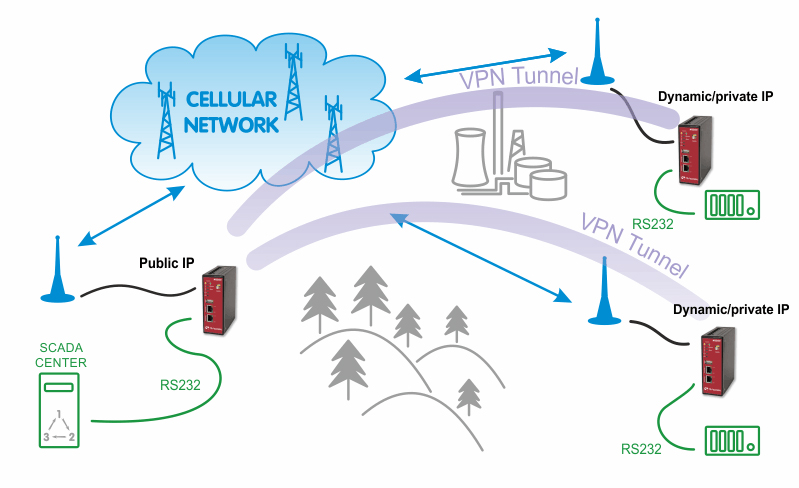
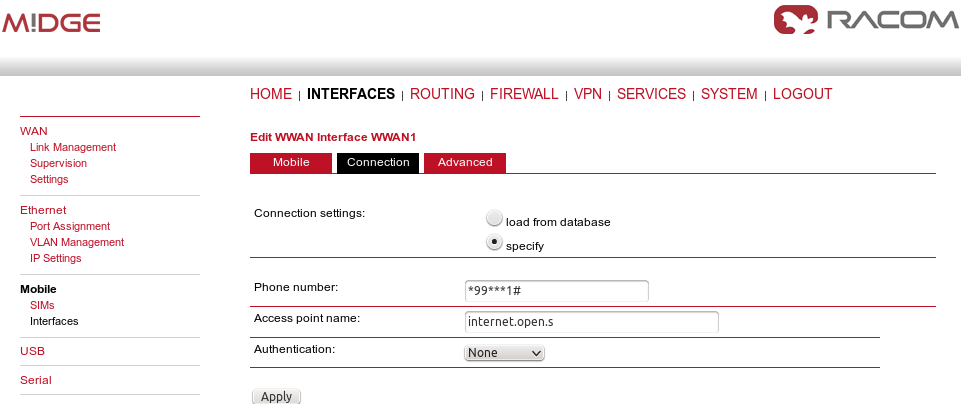
With the public APN, you need to have a public and static IP address in the center. In our example, we configure the APN to be “internet.open.s” so we obtain the required IP address.
The remote stations can be configured with the most basic APN, e.g. “internet” to obtain the private and dynamic IP address. In the next section, we will configure the VPN tunnel which is necessary for this kind of connection. Without the tunnel, the serial communication will be blocked within the cellular network.
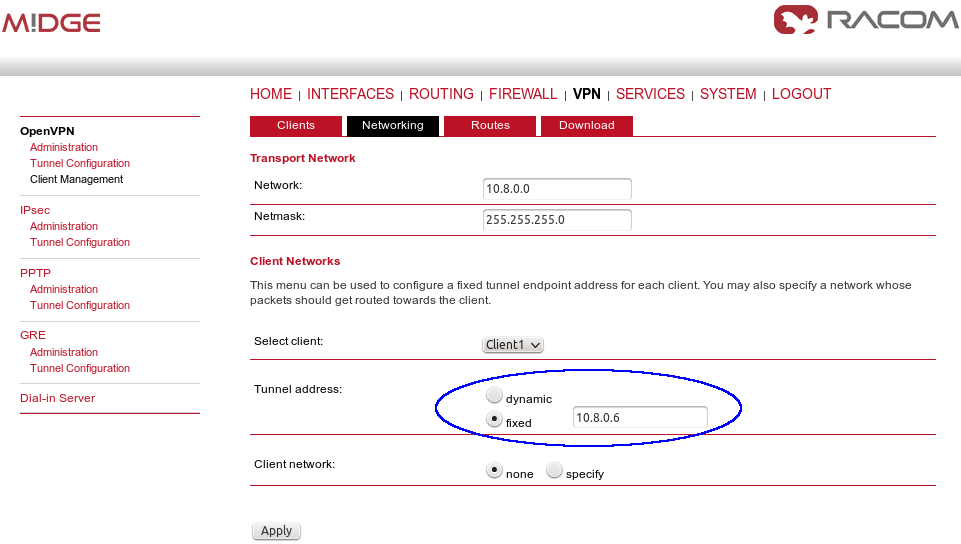
In this example, we configure the OpenVPN tunnel in the routed mode. See Open VPN for configuration details. The only difference is that we do not need to configure any VPN connected networks on any M!DGE unit, we just use the fixed tunnel addresses for serial data communication.
The clients can be then configured just via the Expert files downloaded from the Master M!DGE. The first client will obtain 10.8.0.6 tunnel address and the second client 10.8.0.10.
The configuration is the same as explained with the Private APN , but replace the IP addresses.
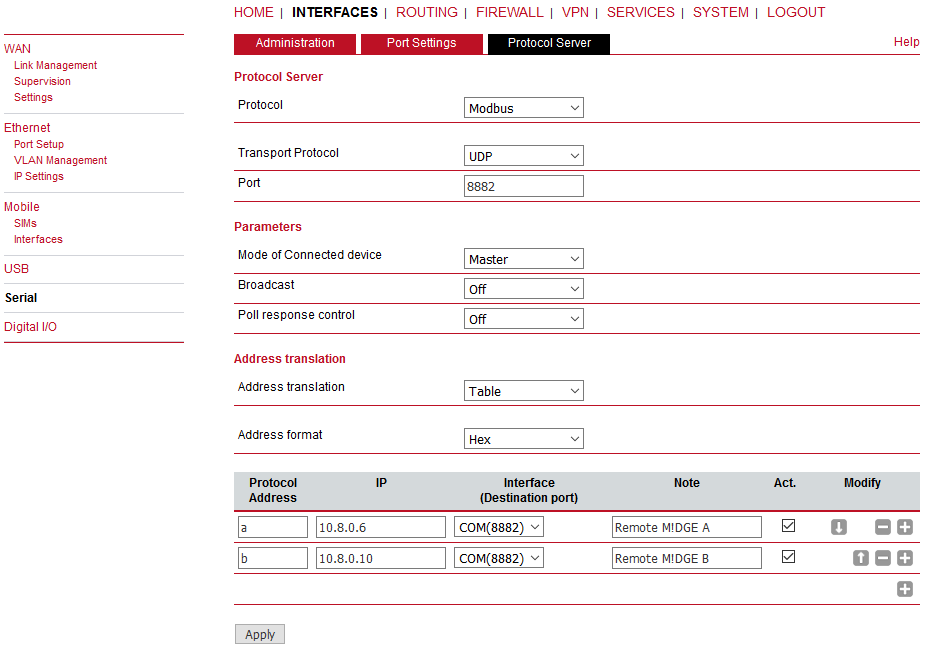
Do not forget to set Poll response control to “Off”, because the VPN changes the IP addresses from WAN to VPN addresses and thus, the protocol mechanism would discard incoming packets.
The Slave must be connected via the OpenVPN tunnel to the Master and its Protocol server must be configured to the Modbus – Slave mode.
| Important | |
|---|---|
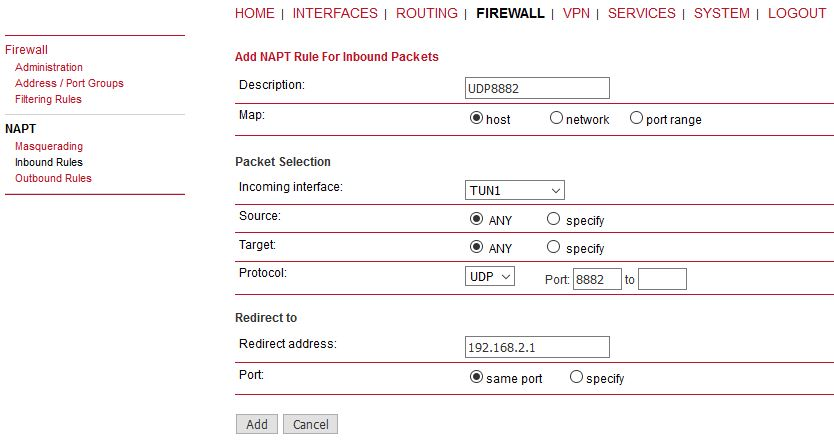
“Protocol server” daemon listens only on LAN1 IP address. This is fixed and cannot be
changed currently (FW 4.4.40.101 and older). Port Forwarding is required to be set in
M!DGE units in a way that received data are forwarded to LAN1 IP on UDP port 8882.
Received interface can be the WWAN IP, OpenVPN TUN interface etc. |
The troubleshooting is the same as explained in the Section 1.4, “Troubleshooting”.
| Note | |
|---|---|
If your server is using TCP connection, configure the Device server instead of Protocol server and set the Mode to “TCP Raw” with the appropriate TCP port. |