To access our SNMP values, any Network Management System (NMS) can be used. However, we recommend using the ZABBIX open source monitoring system. It can be downloaded at: http://www.zabbix.com/download.php.
Zabbix features are explained here – https://www.zabbix.com/features.
If you have chosen the Zabbix software, please read the following pages where we offer a basic Starting Guide to RipEX and Zabbix co-working.
Whatever your choice of NMS, these sections may provide general hints and tips anyway.
| Note | |
|---|---|
The following guide was tested with Zabbix LTS version 6.0. If you have older Zabbix releases, check the RipEX Archive download section for previous versions of this application note. |
Take the opportunity to remotely access and test a live Zabbix demo. See the credentials within the text on the given link.
Follow the Zabbix documentation, download packages from https://www.zabbix.com/download and install Zabbix 6.0 LTS. We suggest using Debian11 (or newer) OS, MySQL database and Apache web server, because of our good experience and knowledge. If using different solution, our help can be limited.
| Note | |
|---|---|
With previous Zabbix versions, we suggested using CentOS7 and CentOS8, but due to changes in distributing these operating systems, Debian OS seems to be much more appropriate. |
Zabbix also offers paid support – see all the possible support tiers at https://www.zabbix.com/support.
Once Zabbix 6.0 LTS is installed, multiple additional installation steps are required so that you can monitor and maintain your RipEX (and any other RACOM products) network(s). Required steps are explained later within this application note.
We also offer Zabbix 6.0 LTS as a virtual, ready-to-be-used, image. It is called “RACOM Zabbix Appliance” or in short “RZA6”. Within this .ova image, functionality for all RACOM products is already installed and ready to be used. Contact RACOM support to obtain this virtual machine and stay in touch with us for more details.
You can run this RZA6 as a virtual machine, e.g., within your VMware or VirtualBox environment (or any similar one).
Once you finish basic Zabbix 6.0 LTS installation following the Zabbix documentation, you can and should check this part for more details about required steps for RACOM products Zabbix support. The order of explained steps is not so important usually.
| Note | |
|---|---|
If there is any particular Linux command, it is based on Debian11 OS. |
We suggest various applications for future usage:
traceroute
nmap
zabbix-sender
sshpass
All the commands can be installed from the command line with:
# apt-get install traceroute nmap zabbix-sender sshpass
If you need, you can implement sending PDF reports automatically. The installation and functionality can vary from version to version so we do not describe step-by-step procedure here. Use Zabbix documentation for more details.
For RACOM products, multiple steps are required. Upload all the MIBs from respective devices (RipEX in our case) to /usr/share/snmp/mibs/ directory. For a proper functionality, add them to SNMP configuration file /etc/snmp/snmp.conf. E.g.:
mibs +/usr/share/snmp/mibs/MG-MIB.txt mibs +/usr/share/snmp/mibs/RacomRay3.mib mibs +/usr/share/snmp/mibs/RacomRay2.mib mibs +/usr/share/snmp/mibs/RACOM-RipEX-1.0.4.0.mib mibs +/usr/share/snmp/mibs/SNMPv2-TC.txt mibs +/usr/share/snmp/mibs/RACOM-RA2-MIB
Download RipEX Zabbix 6.0 template from RACOM website. Unzip the file and import zbx_export_ripex.yaml into your Zabbix instance in Configuration -> Templates menu via web interface. The template consists of:
approximately 300 Item values (~ 20 tags) which can be read from RipEX units (proprietary OIDs only – i.e., OID starting with 1.3.6.1.4.1.33555.2 prefix). For other general OIDs, use Zabbix predefined templates or do your own templates (e.g., SNMPv2-MIB::sysDescr.0, SNMPv2-MIB::sysName.0, …)
RFC1213 and RS232 OIDs are included
Discovery rules
For the 1.9.7.0 firmware, there are 3 Discovery rules
We use Discovery rules for RipEX radio statistics, remote watched values and backup routes, because these tables consist of individual lines where each line is e.g., another RipEX unit, another alternative path or TX lost counter, individual items must be discovered first.
Once discovered, new Items are automatically created and then, Zabbix handles them as basic Items. The only difference is that if a particular new Item becomes unsupported, Zabbix deletes it automatically after a predefined time.
Default Template settings:
All Items are in Disabled state, except:
Modem temperature (°C), RF power (W), TX lost (%), UCC (V) and VSWR (updated every 30 minutes)
Other update times: 30 minutes, 1 hour and 1 day
All Discovery rules are disabled as well
Update times can vary from 5 minutes to 2 hours
By default, each discovery rule is run every 8 hours
Other important steps are for SNMP traps. Once the trap is received, it is handled by our script and for its proper functionality, the OID cannot be translated to text. Edit the snmptrapd:
# systemctl edit snmptrapd.service --force –full
Change the ExecStart variable:
ExecStart=/usr/sbin/snmptrapd -Lsd -f -p /run/snmptrapd.pid -On
The whole file should be:
# cat /etc/systemd/system/snmptrapd.service [Unit] Description=Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Trap Daemon. After=network.target ConditionPathExists=/etc/snmp/snmptrapd.conf [Service] Type=simple ExecStart=/usr/sbin/snmptrapd -Lsd -f -p /run/snmptrapd.pid -On ExecReload=/bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID [Install]
For a proper functionality of RipEX SNMP notifications, multiple additional steps are required. The following sections focuses on SNMPv2c traps and informs. The SNMPv3 notifications are described later on. Also keep in mind that you could configure RipEX notifications different way (e.g., via SNMPTT) – here is just one approach described.
If not yet installed, install ‘snmptrapd’ daemon and enable it to be run automatically.
Within the downloaded .zip templates from our website, snmptrap.sh script is included. Copy the script into /usr/lib/zabbix/externalscripts/ directory and change the file privileges and make it executable.
# chown zabbix:zabbix /usr/lib/zabbix/externalscripts/snmptrap.sh # chmod +x /usr/lib/zabbix/externalscripts/snmptrap.sh
| Note | |
|---|---|
Your ‘zabbix’ user should be enabled. It should have a HOME directory set to /var/lib/zabbix/ and this user should be able to run the shell. E.g., this command can be helpful: |
# usermod --shell /bin/bash zabbix
Check your ‘zabbix_sender’ path and if required, change it within the provided snmptrap.sh script accordingly.
# which zabbix_sender /usr/bin/zabbix_sender
So, the script has this line inside:
ZABBIX_SENDER="/usr/bin/zabbix_sender";
The script parses the output of each received SNMP trap, selects the appropriate host and declares an associative array containing trap descriptions. Eventually, it sends the whole message to your Zabbix server.
The default path to a LOG file from snmptrap.sh script is /var/log/snmptrap/snmptrap.log. Create the directory and a file manually, if not yet created.
Another required step from the command line is to edit /etc/zabbix/zabbix_server.conf file. Find the appropriate lines and edit them to:
SNMPTrapperFile=/var/log/snmptrap/snmptrap.log StartSNMPTrapper=1
Zabbix, and especially your snmptrapd must know how to authenticate against the received traps/informs. If it is SNMPv2, it is quite easy – you just need to allow particular community strings and also explicitly say that our snmptrap.sh must be executed upon a received trap/inform. Do this via /etc/snmp/snmptrapd.conf file. Example of such file:
authCommunity log,execute public authCommunity log,execute mwl-snmp authCommunity log,execute racom-snmp traphandle default /bin/bash /usr/lib/zabbix/externalscripts/snmptrap.sh
With SNMPv3 it gets more complicated.
For SNMPv3 Informs (not traps), you need to create the user via createUser command. Stop the snmptrapd daemon:
# systemctl stop snmptrapd
Now, edit the /etc/snmp/snmptrapd.conf file and add these lines:
createUser racom MD5 "racom1234" DES "racom5678" authUser log,execute,net racom
This should add the User “racom” with MD5 and DES secrets and authenticate him. Save the changes and start the snmptrapd daemon.
# systemctl start snmptrapd
Now, the SNMPv3 informs can be successfully received and used.
SNMPv3 Traps need a bit different command. Everything is the same, but the EngineID must be configured.
Generate, copy&paste or manually configure RipEX EngineID. This was explained in Section 2.5, “RipEX SNMP Settings”.
| Note | |
|---|---|
The similar procedure must be met for any other SNMPv3 devices and their SNMPv3 traps/informs (not just RipEX). |
Once you apply all the mentioned changes, it is suggested to reboot your Linux OS and check the functionality.
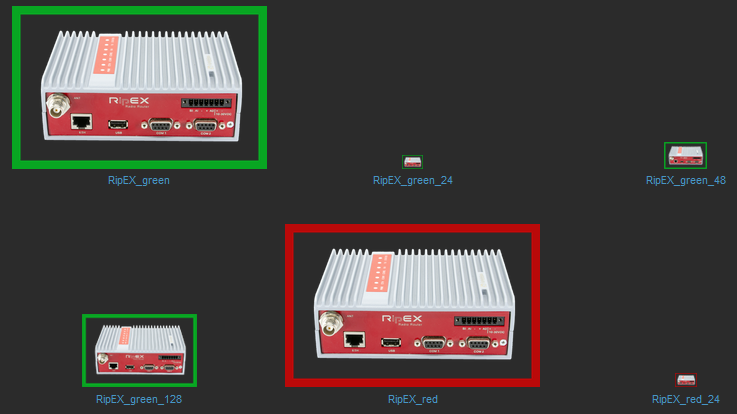
Hosts can be displayed in graphs. For such a purpose, we created multiple RipEX images of different size and with different borders (e.g., red border in case the unit is in a problem state). These images are included in the mentioned .zip file with RipEX template. Import them one by one in Administration – General – Images menu, or via directly via MySQL.
Now, Zabbix should be ready for monitoring RipEX network. This chapter gives you a brief procedure to get started, but feel free to utilize different approach.
First, we suggest to create a Host – probably RipEX Base station accessible via Ethernet from Zabbix. Go to the Configuration – Hosts menu and click on the “Create host” button on top right corner.
Always put the IP address of the unit to the “Host name” field so the SNMP notifications work (the script works with IP addresses). The “Visible name” can be set to any required value.
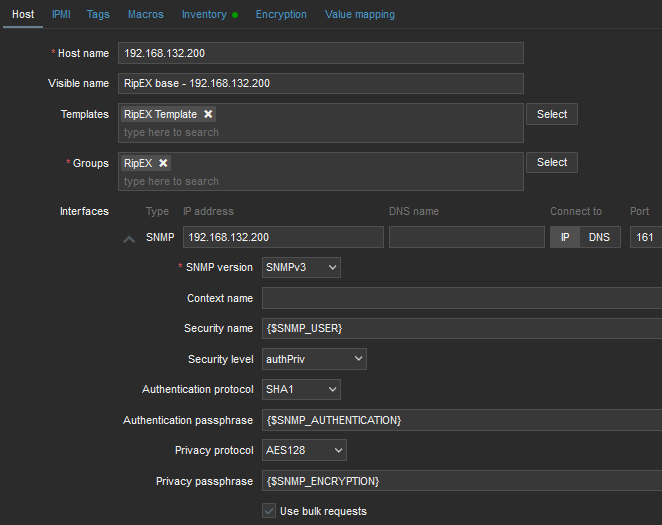
Select the “RipEX Template” so that the unit is preconfigured with all RipEX supported Items. Create a new, or add it to an existing one, RipEX group. You can name it as required – e.g., based on RipEX network location or particular customer company name. Set the SNMP Interface:
IP address
Port (usually UDP/161)
SNMP version (either v2c, or v3)
If v2c, set the community string to MACRO {$SNMP_COMMUNITY}
If v3, set the values according to your RipEX setup
Security name – {$SNMP_USER}
Authentication passphrase – {$SNMP_AUTHENTICATION}
Privacy passphrase – {$SNMP_ENCRYPTION}
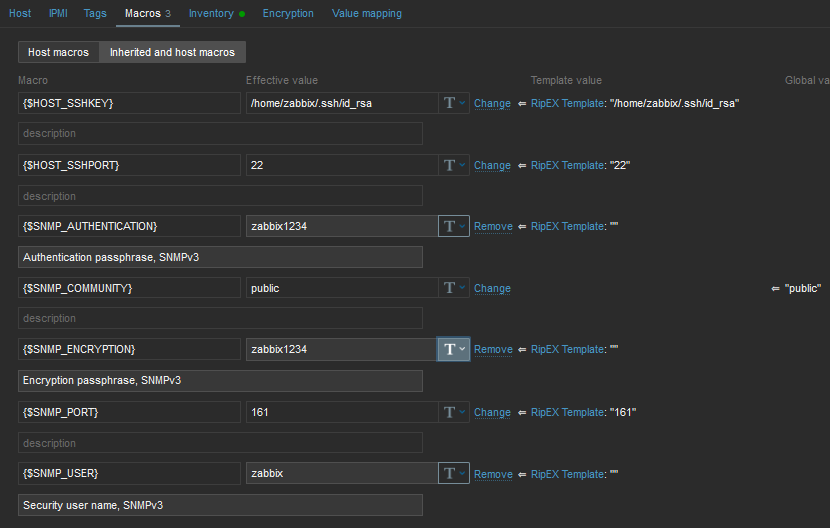
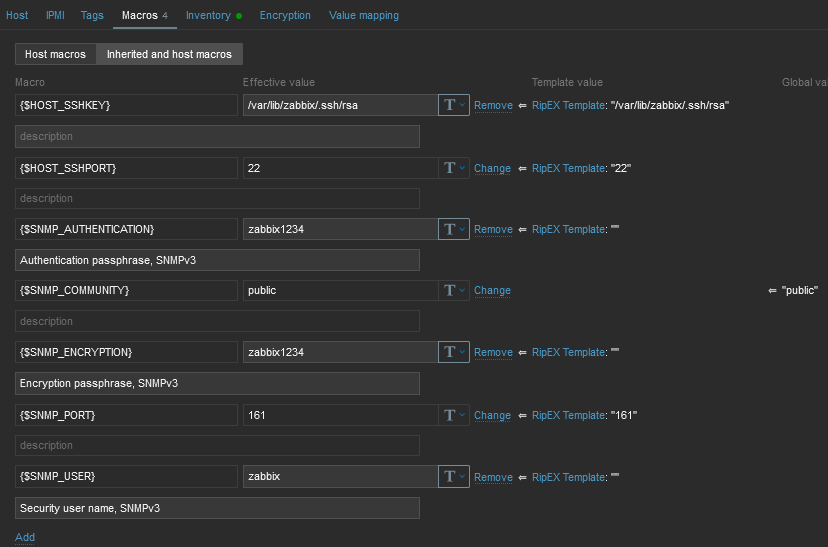
Now, check and change MACROs in “Macros” tab
HOST_SSHKEY and HOST_SSHPORT macros are used for RipEX scripts
You can either change the values in Template so it is the same in all your RipEX units, or you can set it per Host.
Check the “Use bulk requests” option because it optimizes data traffic being sent
Verify the Inventory tab – it should be set to “Automatic” so some of the values are automatically filled by SNMP queries. Click on the “Add” button – a new Host is created.
But the host is not monitored yet, because all the Items and Discoveries are disabled by default.
Only monitor the values which you really need and with reasonable update times. This is important for units accessible via the Radio channel – so that you limit data being sent over the narrow RipEX radio network.
A template keeps up to 1 year of trends/history.
Go to the Host’s Items and enable required Items, you can also edit the SNMP query intervals and other parameters.
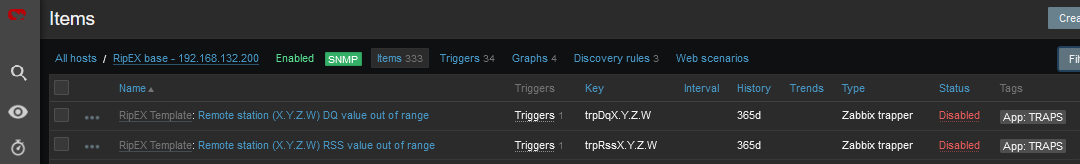
If you want Traps/Informs to be working, you need to enable particular traps with App tag equal to TRAPS and enable Triggers accordingly (i.e., if you enable “TX Lost value out of range” Item, you also need to enable a Trigger for this Item).
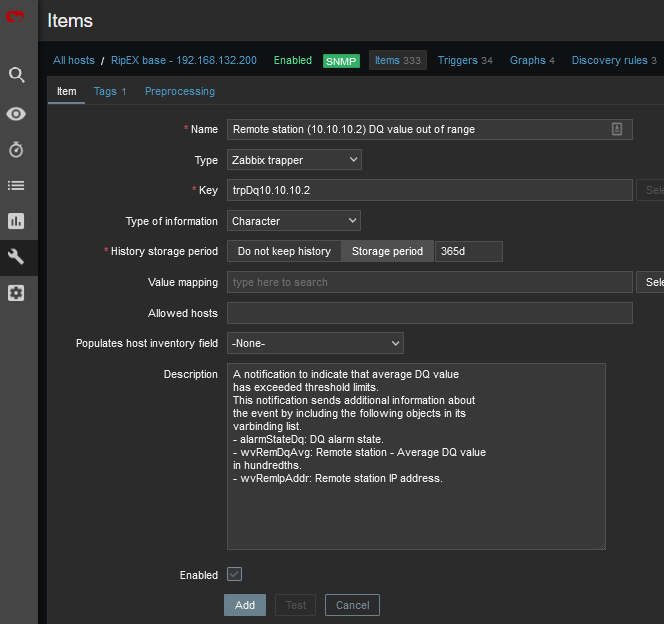
RSS and DQ trap items are disabled in the template by default. The reason is that we need to define remote RipEX IP addresses first. See the following example for enabling a DQ trap.
Go to the Zabbix web front-end and select a RipEX host for which you want to process DQ traps. Click on the Items button and find an item with the following key: trpDqX.Y.Z.W.
Click on the item and then click on the Clone button. Now you can edit the item. Replace the “X.Y.Z.W” string in the item Name with the remote RipEX radio IP address (e.g. 10.10.10.2). Do the same in the Key field and select the Enabled option in the Status field. See the following example:
Save the changes and open the host Triggers list. Repeat the above steps for the DQ trigger and save the changes. You should see the trigger with the enabled status.
Follow the same procedure (DQ and RSS) for other remote RipEX units as needed.
Last important menu is “Discovered rules”. They are already explained on previous pages. If you want to discover particular Items, just enable required Discovery rule(s). E.g., enable “Discovery – Remote watched values” for receiving values from Statistics table containing RSS, DQ, remote VSWR etc. with all neighbouring RipEX units.
You can check the data in the Monitoring – Latest data menu. Filter the values are required. All numeric values can be depicted in graphs. String values have their own history.
Other units can be easily added by a “Clone” button from this Host configuration. Just change appropriate IP addresses and ports. Divide them into groups (e.g., geographically). Choose wisely the monitored values and enabled discovery rules.
This application note cannot target all possible information about Zabbix and its usage. Check Zabbix documentation and Google forums for general help and guides. The following section provides several hints and tips for quicker and easier RipEX network monitoring. Information provided might not be fully explained or might be different in any other Zabbix version other than 6.0 LTS.
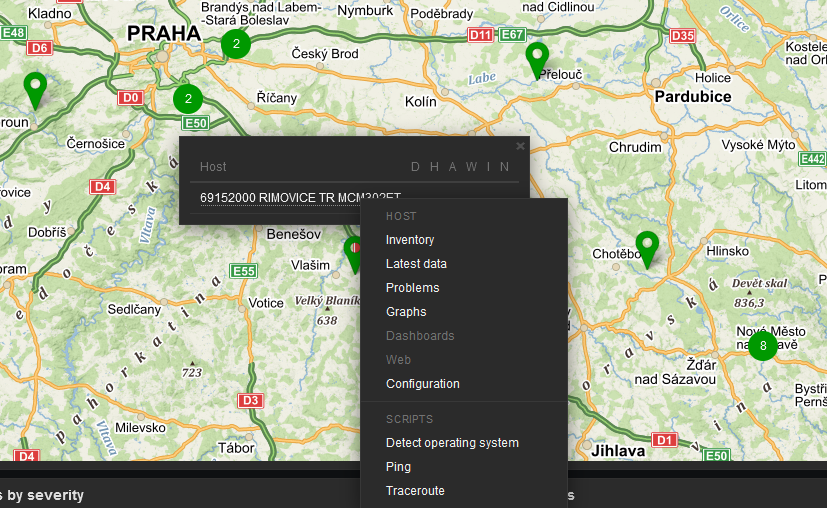
Having a map is handy way for a network overview. On a single map, or multiple maps (even hierarchical) you may see all RipEX units (and any other devices) and their status overview. There can be a plain/empty background, or e.g., some picture of a map (static).
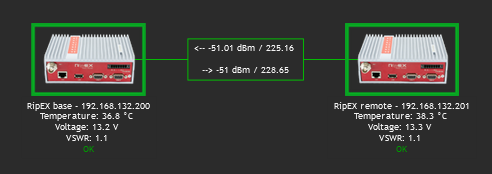
On the map above, we can see two RipEX units with a displayed name and current Radio temperature, voltage and VSWR. If the unit has no Problem, an “OK” message is displayed and the Host borders are in green color. We also depict a radio link between these units and its RSS/DQ values.
Host details:
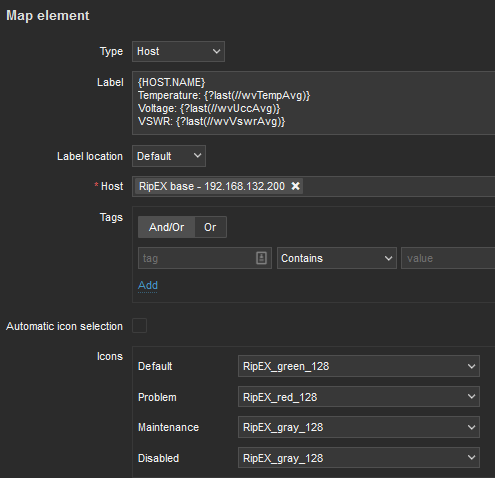
Label is set as follows:
{HOST.NAME}
Temperature: {?last(//wvTempAvg)}
Voltage: {?last(//wvUccAvg)}
VSWR: {?last(//wvVswrAvg)}Select a particular host and you can change icons for various situations.
Example of the link Label:
<-- {?last(/192.168.132.200/wvRemRssAvg[10.10.10.2])} /
{?last(/192.168.132.200/wvRemDqAvg[10.10.10.2])}--> {?last(/192.168.132.201/wvRemRssAvg[10.10.10.1])} /
{?last(/192.168.132.201/wvRemDqAvg[10.10.10.1])}Even the link color can change in time – for example lower RSS than -90 dBm. You can create your own Trigger monitoring average RSS values.
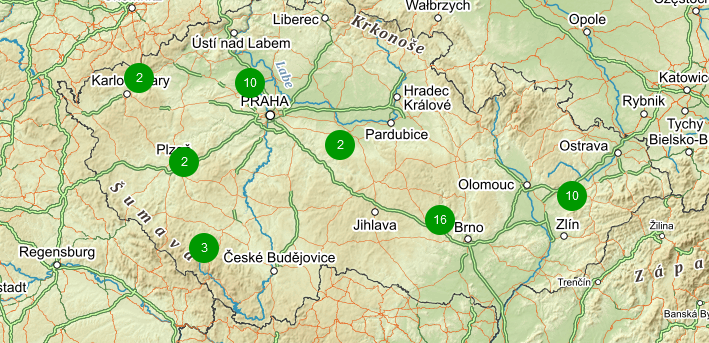
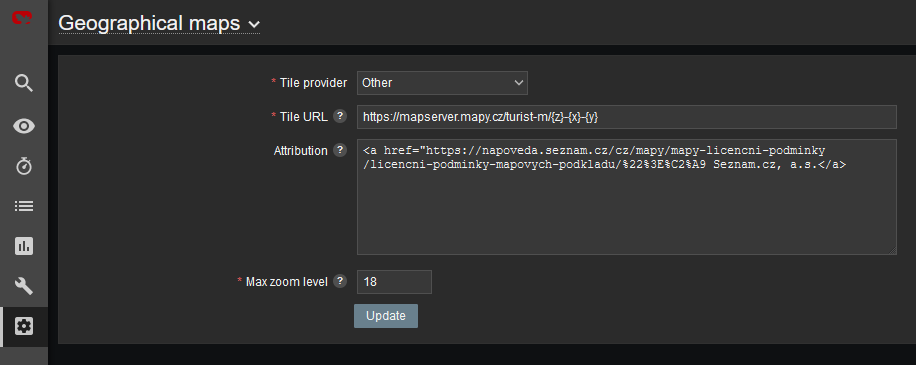
New feature from 6.0 LTS Zabbix version are Geographical maps. If you add GPS coordinates to your RipEX hosts, you can display them on geographical maps.
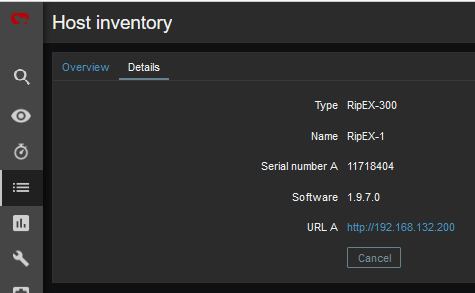
First, you need to add GPS coordinates in the Host Inventory.
Another step is to enable and configure Geographical graphs. Go to Administration – General – Geographical maps menu. Set the required map source/provider. There is a list of default supported map sources, but you can also add “other”. Here is the example for Czech mapy.cz map source.
Tile URL: https://mapserver.mapy.cz/turist-m/{z}-{x}-{y}
Attribution:
<a
href=”https://napoveda.seznam.cz/cz/mapy/mapy-licencni-podminky/licencni-podminky-mapovych-podkladu/%22%3E%C2%A9
Seznam.cz, a.s.</a>
Max zoom level: 18
The last step is to add Geographical map to your Dashboard. Edit the dashboard and add “Geomap” widget. Select its name, host group(s) and host(s). Save the changes.
Within the map, you can use a “zoom” feature. You can either see multiple hosts within one icon, or one icon is one host (it is zoomed enough). You can then be forwarded into particular menus etc. Color of the Icons can be changed upon Host status. Read more in Zabbix documentation.
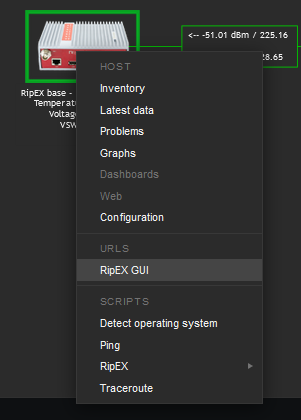
Units’ GUI can be accessed from Zabbix web interface from multiple menus.
A typical one is from simple maps. Configure the URL within the Host on the map and once you click on the Host in this map afterwards, you can be forwarded there. Keep in mind it is not possible from geographical maps.
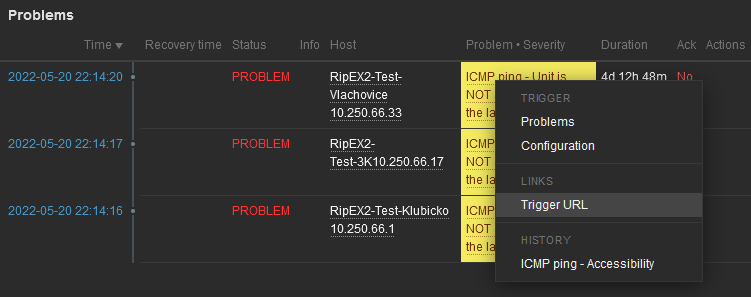
Another way is a link from Triggers so that if a Problem occurs, you can quickly go to the required web interface.
The third option is to use Inventory for configuring URL. For every Host, you can enable the Inventory (serial number, OS, host type, …). Within many Inventory options, the URL can be defined.
Another useful feature is generating scheduled reports. You need to configure Scheduled reports in general. Once you have it, go to the Report – Scheduled reports menu and create a new one. Basically, Zabbix can send multiple users in regular intervals its Dashboard(s) as PDF.
More information e.g., see Zabbix website.
In case of any issue within your network, e.g., drop in the signal quality, or the unit being unreachable, Zabbix can automatically send an e-mail to predefined e-mail addresses. See the following example for your reference, but customize it to suit your needs.
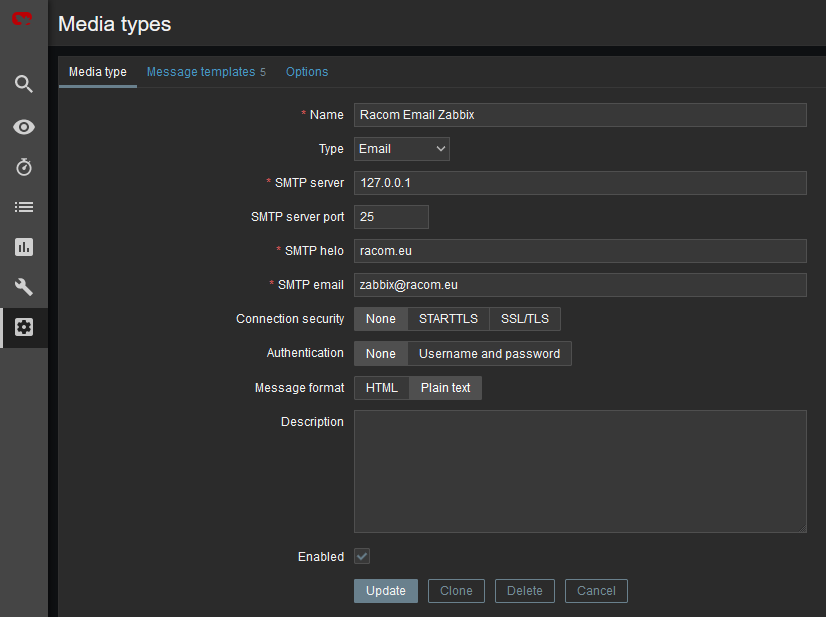
The e-mail can be set in the Administration – Media Types menu. Edit the E-mail type corresponding to your server settings. In our example, we use our own SMTP server reachable from Zabbix server. No special security or password is required. You should be able to use any SMTP server.
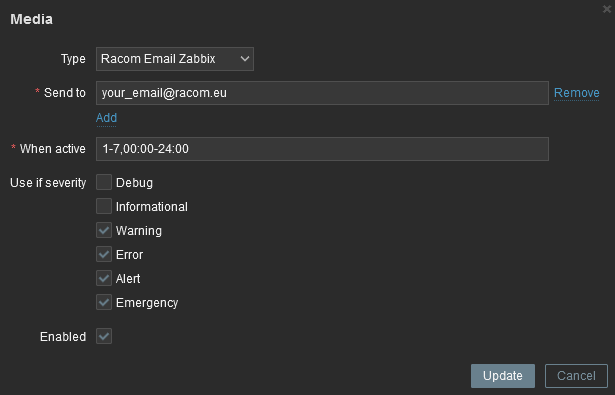
The e-mails are sent to the users’ e-mail addresses. Go to the Administration – Users menu and configure the required e-mail addresses within the user’s details (Media).
You define the time when the e-mail will be sent (e.g., do not send it over the night) and the severity of the issue (e.g., send me the e-mail just in case of a critical issue).
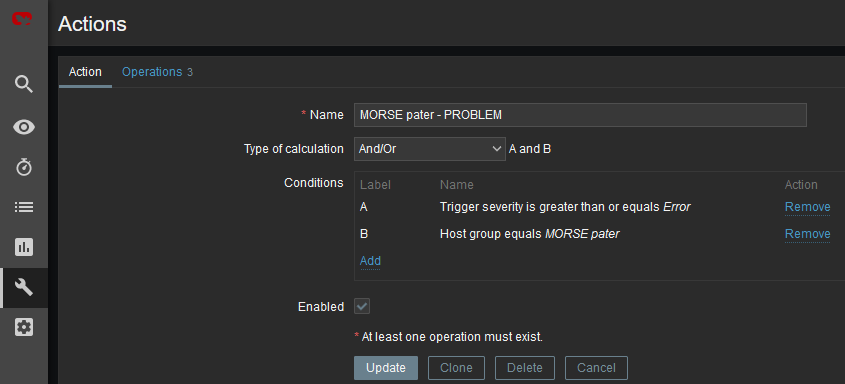
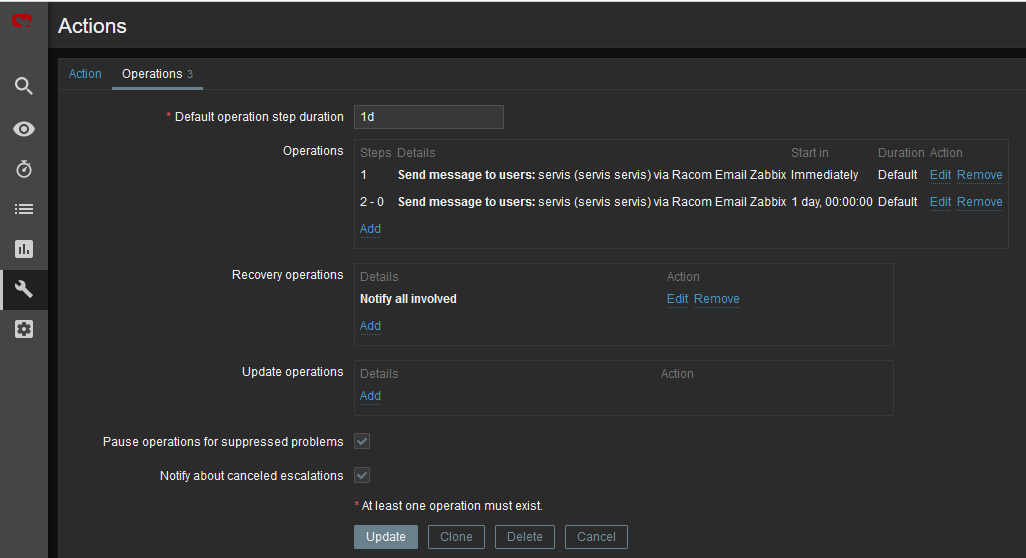
The last step is to configure the action – configure which issue causes the e-mail to be sent. Go to the Configuration – Actions – Trigger actions menu and create a new Action. Set a Name of the Action and its Conditions – trigger severities and host group are used within the screenshot below.
Within the Operations tab, define one or multiple operations. In the example, once the Problem occurs, Zabbix sends an email. It sends such email every other day until the problem is fixed.
We also send a Recovery email to all involved recipients.
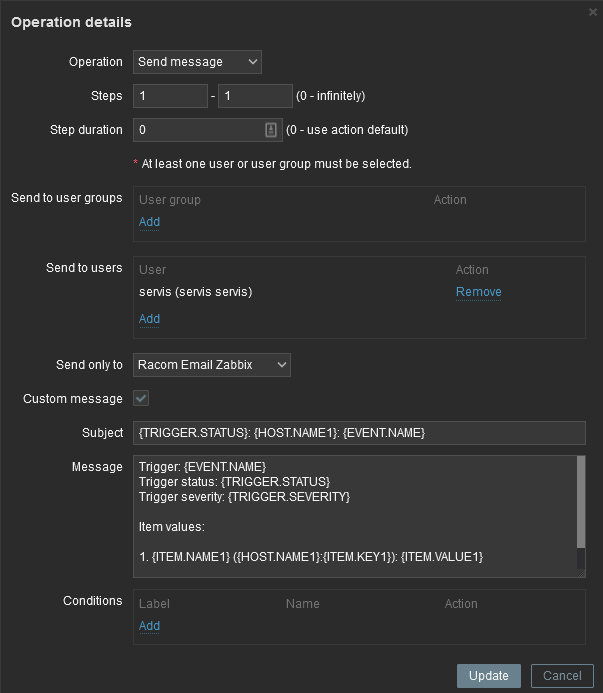
Usually, you will use the MACROs for the e-mail body/subject. In this example, the Subject of the email will consist of the host’s Name, Trigger status (Problem or OK) and Event Name. Within the body of the message, there can be additional information such as the Trigger Severity, URL and the Issue details.
By default, there are no ready-to-be-used actions in Zabbix such as configuration backup or firmware upgrade. The Zabbix NMS is a general system which requires special features to be implemented by RACOM or by the user himself.
We provide the user with a guide how to use and define these special features and within the RipEX template, we already prepared several examples:
Configuration backup
Displaying the current RSS
| Note | |
|---|---|
If you have troubles running those scripts or making your own, contact us on support@racom.eu. |
The whole implementation can be quite time consuming, but once you successfully run the first script, the others are very similar and its implementation is straightforward.
Within the Template, there are two scripts. As you realize, having the configuration backup files can be crucial if replacing the unit. There is nothing easier than just uploading the configuration file into a brand new RipEX unit.
Before creating and running the first scripts, you need to prepare the Zabbix server (and the Linux operating system). In this example, we configure the Debian11 OS with Zabbix 6.0 LTS installed via packaging system.
The following steps can be done in different order, but following this order is absolutely fine.
By default, the zabbix_server configuration file is located in the /etc/zabbix/zabbix_server.conf file. Find the line with “SSHKeyLocation” parameter and define it with this value:
SSHKeyLocation=/var/lib/zabbix/.ssh
This is the location of the private SSH key which will be used to access the RipEX units. Restart the Zabbix server afterwards.
systemctl restart zabbix-server
The scripts must be uploaded manually to a correct directory. The default directory is /usr/lib/zabbix/externalscripts/. Copy the script files from the ZIP Template file to this directory. The target state should look similar to this output:
ls -l /usr/lib/zabbix/externalscripts/ -rwxr-xr-x 1 zabbix zabbix 686 May 4 10:21 ripex_cli_cnf_textfile_get.sh -rwxr-xr-x 1 zabbix zabbix 111 Mar 8 2016 ripex_cli_rss_show.sh -rw-r--r-- 1 zabbix zabbix 9612 May 25 09:31 script-log.txt -rwxr-xr-x 1 zabbix zabbix 39262 May 26 08:44 snmptrap.sh
There are two executable scripts via the Zabbix web interface (starting with “ripex_”). The LOG output of those scripts is in script-log.txt file. There is also the snmptrap.sh file which you should have there for the SNMP TRAP/INFORM functionality.
Make sure that the files have the zabbix user/group and are executable.
# chown zabbix:zabbix /usr/lib/zabbix/externalscripts/* # chmod +x /usr/lib/zabbix/externalscripts/*.sh
The Zabbix user cannot login to the bash by default. We need to enable it as follows (if not already done in RZA6).
usermod --shell /bin/bash zabbix
If not already created, create the HOME directory for the Zabbix user.
usermod -m -d /var/lib/zabbix zabbix chown zabbix:zabbix /var/lib/zabbix chmod 755 /var/lib/zabbix
Create the directories for the saved configuration and firmware files and change the access rights.
mkdir /var/lib/zabbix/configuration-backup mkdir /var/lib/zabbix/configuration-backup/ripex chown -R zabbix:zabbix /var/lib/zabbix/
The directory for the SSH key should now be located in /var/lib/zabbix/.ssh directory. Change the current directory to this one and login as zabbix.
su zabbix
A new prompt appears. We need to upload the SSH keys into every unit we want to control. You can either have you own RSA/DSA key or you can create a new one following this example. Run
ssh-keygen -t rsa
Follow the guide of the ssh-keygen application and leave the passphrase empty. To copy our RSA key into RipEX units, copy the public part of the key and run the following command:
ssh admin@192.168.132.200
Just replace 192.168.132.200 with the correct RipEX IP address. The prompt will ask for the admin password, fill it in and click Enter. Now, you should be logged in RipEX CLI. Run the following command:
vi .ssh/authorized_keys
| Note | |
|---|---|
Browse the Internet for how to use ‘vi’ text editor if you are in trouble. |
Insert (paste) your public part of the key to a new line. Save the changes and close the file. Logout and check, if you can access the unit without a password.
ssh -i rsa admin@192.168.132.200
We completed all Linux tasks, but we still need to edit Zabbix web interface.
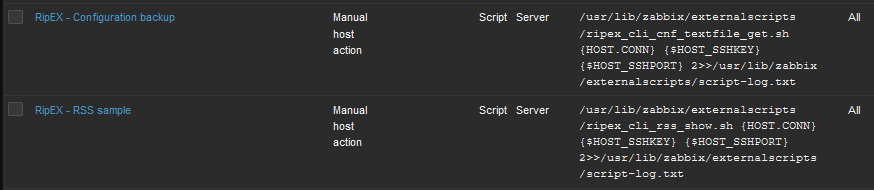
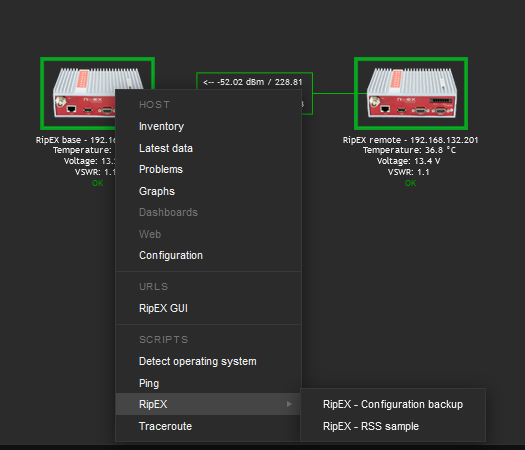
Scripts must be manually created in the Zabbix Administration – Scripts menu. See the example below and create Zabbix scripts for RipEX units.
If you open one of them, you can modify them as required. If you do not have any, you need to create them from scratch.
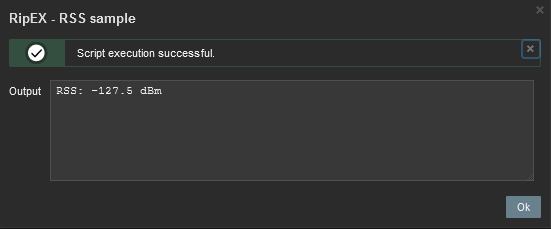
RSS sample – this script runs the RipEX Maintenance – RSS sample feature. The current level of Received Signal Strength (one sample) on Radio channel is measured. This sample is measured regardless of the current Radio channel status (Quiet/Rx/Tx).
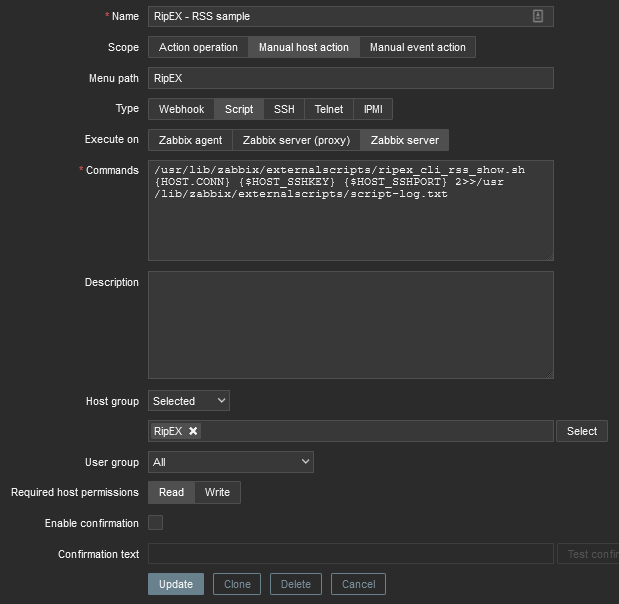
Name: RipEX – RSS sample
Scope: Manual host action
Menu path: RipEX
Type: Script
Execute on: Zabbix server
Commands: /usr/lib/zabbix/externalscripts/ripex_cli_rss_show.sh {HOST.CONN} {$HOST_SSHKEY} {$HOST_SSHPORT} 2>>/usr/lib/zabbix/externalscripts/script-log.txt
Set other parameters to suit your needs.
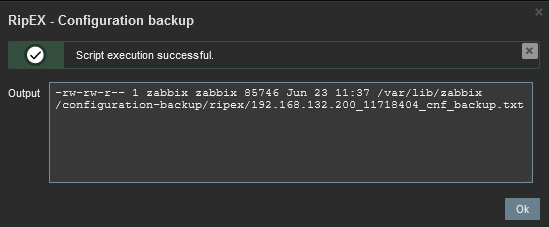
Configuration backup – the script creates a configuration backup file in /var/lib/zabbix/configuration-backup/ripex/ directory. The name is taken from RipEX S/N and Ethernet IP.
All is the same, except the “Commands” parameter:
/usr/lib/zabbix/externalscripts/ripex_cli_cnf_textfile_get.sh {HOST.CONN}
{$HOST_SSHKEY} {$HOST_SSHPORT}
2>>/usr/lib/zabbix/externalscripts/script-log.txt
The parameters are MACROs which should be enabled by default due to our Template. Each RipEX unit uses the SSH port 22 and the SSH key saved in /var/lib/zabbix/.ssh/rsa file by default. If you need to modify any of these parameters, go to the Configuration – Hosts menu and edit the particular Host’s MACROs.
Test the scripts now. Scripts are e.g., available from maps.
The easiest script displays the RSS sample. The level (in dBm) should be displayed within several seconds in the pop-up window.
Another script is the Configuration backup. The expected output should display a full path to the stored file.
Zabbix 6.0 LTS offers you to use your own company’s branding instead of Zabbix ones, or RACOM logos in case of using RZA6.
General and brief procedure is described here:
https://www.zabbix.com/documentation/current/en/manual/web_interface/rebranding
For the RZA6, we created a file /usr/share/zabbix/local/conf/brand.conf.php with this content:
<?php return [ 'BRAND_LOGO' => 'racom/racom_logo.png', 'BRAND_LOGO_SIDEBAR' => 'racom/racom_logo.png', 'BRAND_LOGO_SIDEBAR_COMPACT' => 'racom/racom_logo_compact.png', #'BRAND_HELP_URL' => 'https://www.racom.eu/ APP NOTE LINK ' ];
Logos were scaled to 140×20 and 20×13 (compact one). The logos are placed in /usr/share/zabbix/racom/ directory. After these changes, the Login screen can look like:
If you need any additional help or information, do not hesitate to contact support@racom.eu. We are ready and happy to help you.
We do recommend using our RZA6 solution. If not in your real network, then as a start for getting familiar with RipEX SNMP and Zabbix NMS, because RZA6 has many configuration steps pre-configured and done.