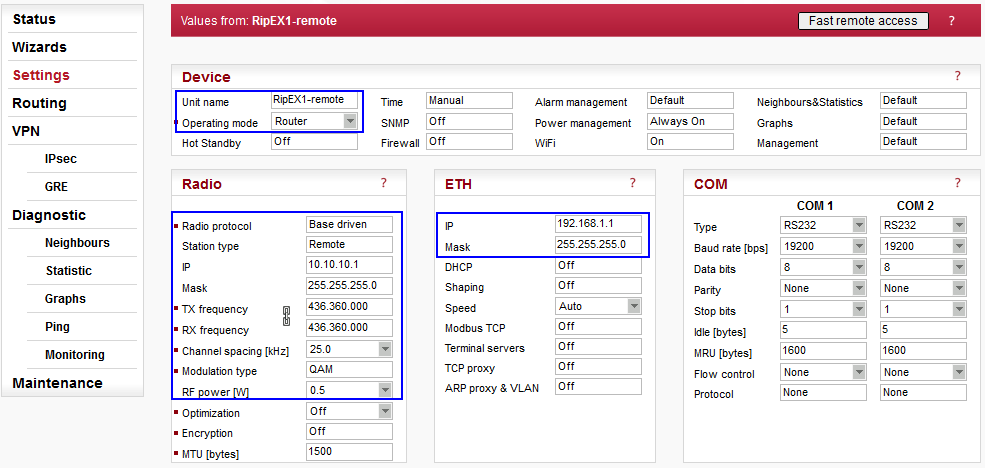
Parameters:
| Unit name | “RipEX1-remote” |
| Operating mode | “Router“ (IPsec cannot be used in the Bridge mode) |
| Radio protocol | “Base Driven“ (The protocol can also be set as “Flexible”, but this example utilizes the Base Driven Protocol, BDP) |
| Station type | “Remote” (detailed configuration in Fig. 4.2) |
| IP/Mask | “10.10.10.1/24” (common subnet for all RipEX units in this example) |
| TX/RX frequency | “436.360.000 MHz” (configure any frequency, but the same among all RipEX units – the simplex or duplex scenarios are possible) |
| Channel spacing | “25 kHz” (configure any spacing, but this must be the same for all units) |
| Modulation type | “QAM” (use the same “type” for all units, otherwise configure as preferred) |
| RF power (W) | “0.5 W” (set the minimum possible RF power for tests using dummy loads on your desk – laboratory tests) |
| ETH IP/Mask | “192.168.1.1/24” (set the Ethernet IP/Mask) |
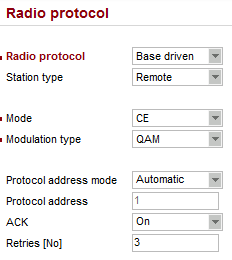
Parameters:
| Radio protocol | “Base driven” |
| Station type | “Remote” |
| Modulation type | “QAM” (must be the same among all RipEX units) |
| Protocol address mode | “Automatic” (protocol address equals to the last Radio IP digit, i.e. “1”) |
| ACK | “On” |
| Retries | “3” |
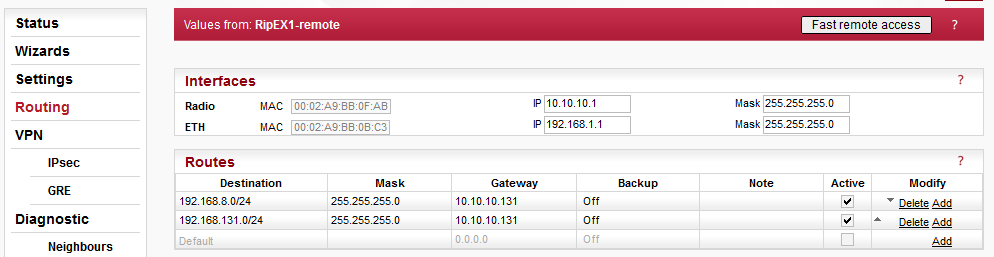
Two routing rules must be added – both remote Ethernet subnets are accessible via the Master radio IP. Without correct routing rules, IPsec will not function properly.
192.168.8.0/24 via 10.10.10.131
192.168.131.0/24 via 10.10.10.131
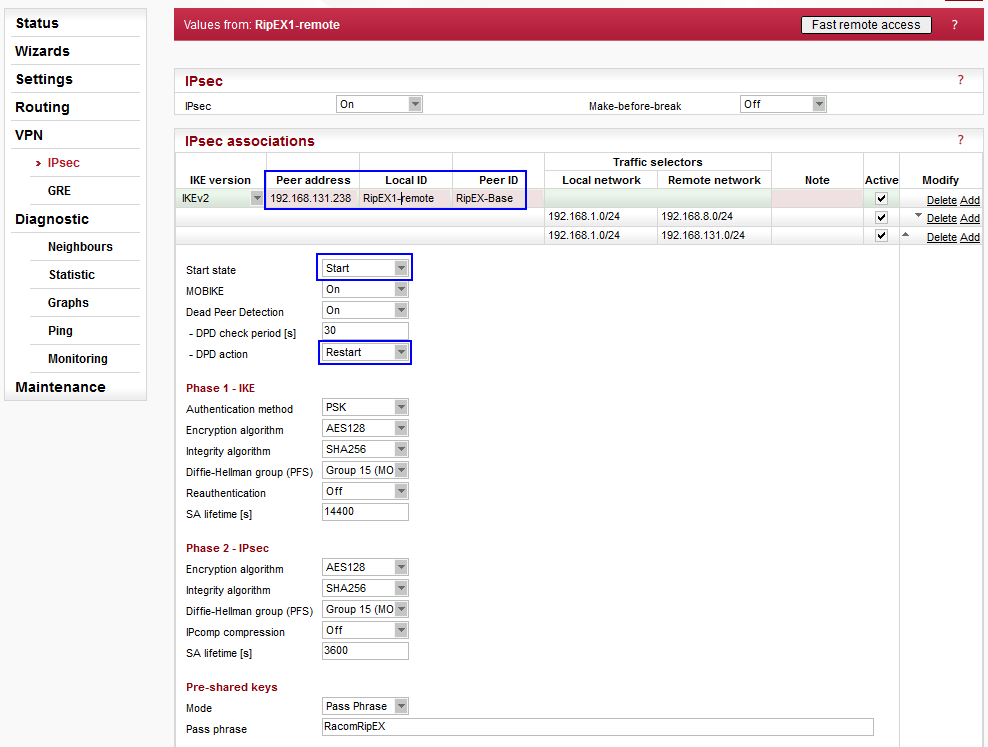
Parameters:
The IKE,
IPsec and PSK parameters are the same as on the Master station. Remember
the following differences:
| Peer address | “192.168.131.238” (“RipEX-Base” Ethernet IP) |
| Local ID | “RipEX1-remote” |
| Peer ID | “RipEX-Base” (both IDs must correspond to those used on the Master station) |
| Traffic selectors | “192.168.1.0/24 (local) <-> 192.168.8.0/24” (a selector for RipEX1-remote and RipEX2-remote connectivity over IPsec) “192.168.1.0/24 (local) <-> 192.168.131.0/24” (a basic selector for Ethernet to Ethernet accessibility over IPsec) |
| Start state | “Start” (Connection is established immediately) |
| DPD action | “Restart” (Connection is established immediately) |
The “Start state” might either be “Start” or “On demand”, but cannot be “Passive”, because this state is already configured on the Master station and no end-point would initiate the VPN tunnel.