| Note | |
|---|---|
Apply for software version 505 and above. |
The CNI (Channel to Node Interface) menu is identical for all types of channels. It is described in chapter Chapter 25, CNI-channel to node interface
Let’s note that the IP-M-IP and Morse Application Server communication use the user output but M-IP-M uses the retranslation output, see later.
The external form of the menu:
Channel to Node Interface:
retranslation | user lim
id N A t m | N A t Base m sec brc S e
(0) 0 NO AR | 1 MASK 00000000/08 ON OFF NONE
de(f)ault (r)ead (w)rite
(I)nit (S)ync
(q)uitFrom MORSE main menu type Ehe Enter Enter
Ethernet: (e)nable:ON (s)peed:auto bps (p)romiscuous mode:OFF d(u)plex:auto (T)imer init level:0s Eth. adr(H)i:0002h Eth. adr(M)i:A953h Eth. adr(L)o:73B7h (R)XQ depth:16 R(X)Q count:16 (z)Status phy Restart (i)nit level:FEC (d)sc: 5810 de(f)ault (r)ead (w)rite (I)nit (S)ync (q)uit >>
The default values are recommended in this menu. The others are suitable for service or development purposes.
Meaning of items:
From MORSE main menu type EPe Enter Enter.
Internet Protocol: Eid| ip address | net mask | gw | (0) C0A80009 192.168.0.9 FFFFFF00 255.255.255.0 00000000 0.0.0.0 de(f)ault (r)ead (w)rite (I)nit (S)ync (q)uit >>
Continue by: 0 Enter
Etp: (i)p adr:C0A80009h (g)ateway adr:00000000h (n)et mask:FFFFFF00h (G):0000 (d)sc: 6029 AR(P) parameters parame(t)ers de(f)ault (r)ead (w)rite (I)nit (S)ync (q)uit >>
Meaning of items:
ARP: (A)RP ttl:30s A(R)P timeout:50ms proxy arp (m)ode:NORMAL Proxy Arp (B)ase:00000010 Proxy Arp (M)ask:000000F0 (p)rint ARP table (c)lean ARP table (s)ave ARP table (r)estore ARP table ipg(W) restart (q)uit >>
| (A)RP ttl: 30s | — time of life ARP record |
| A(R)P timeout: 50ms | — timeout for ARP answer |
| proxy arp (m)ode | — next three parameters define, to which ARP request should Ethernet channel send the answer WARNING — the
setting
See the example in the MORSE Guide 3. |
| (p)rint ARP | — displays the current ARP table |
| (c)lean ARP | — erases the ARP table |
| (s)ave ARP | — saves the ARP table into NVHeap memory |
| (r)estore ARP | — reads the ARP table from NVHeap memory |
| ipg(W) restart | — restarts the ipgw protocol |
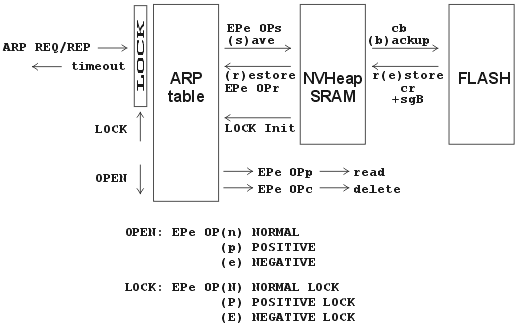
Locking table ARP (fw 10.0.94.0 and higher)
Table ARP changes dynamically. After an exchange of ARP REQ, ARP
REP frames a new item is added to the table or its record is updated
with the term of validity. Once its lifetime has been reached the record
is deleted. This dynamism can be switched off by locking the table using
command proxy arp (m)ode:...LOCK. The analogue version of
proxy arp mode needs to be used for locking, e.g. for NORMAL use NORMAL
LOCK. Then the Ethernet protocol communicates only with IP addresses
contained in the located table ARP. It only responds to ARP REQ from
addresses contained in the table and it doesn’t delete old records from
table ARP. This limits the transmission of frames from unknown IP
addresses. The procedure for locking :
Undertake standard configuration over the Eth channel, e.g. in NORMAL mode.
By using
(p)rint ARP tablecheck that all necessary records in the table have been created.Save the table to NVHeap memory using command
EPe 0Ps. The status of table ARP at the point of saving is decisive for operation in LOCK mode.Backup the record in NVHeap memory to Flash memory using command
cb, which means(c)onfigure (b)ackupLock table ARP for example using command NORMAL LOCK:
EPe 0PmN,(q)uit,(I)nit,(W)rite. In this way the status from NVHeap memory is transferred into the table.Check the content of the locked table ARP using command
EPe 0Pp. The table must contain records for all those participating in future communications. The validity period of the record equals zero.This procedure can also be carried out when needed in other CUs at the MORSE – IP interface.
Additional manipulation with the table:
The table cannot be locked sooner than it is saved using command
(s)ave ARP table. Otherwise communication over Ethernet will be blocked either immediately or after restarting the CU.Reading of the saved table is done during initialisation of the mode
proxy arp (m)ode:LOCK, i.e. during start up in LOCK mode.During start up with a discharged backup battery the configuration (including that of the ARP table) is restored from flash memory, and for that reason back up needs to be carried out using command
cb.The status of the table stored in NVHeap can be ascertained from menu
EPe 0Pusing commands(r)estore ART tableand(p)rint ART table.
An overview of the behaviour of the locked table ARP :
Timeouts are off and records can’t be deleted.
When sending frames to the Ethernet network ARP is not sent. Frames can only be sent to IP addresses contained in the table.
Receipt of frames from the Ethernet network is only possible from addresses which comply with a combination of IP and MAC contained in the table. All other frames are discarded.
The Ethernet protocol only responds to queries from ARP REQ, whose IP and MAC are already contained in the table.
The Ethernet protocol does not write new items into the table.
During an exchange of hw at some of the communication participants communication with them is interrupted (change of MAC address).
Transparent representation of the described processes :
An example of a printout of a current (unlocked) table ARP:
ARP cache: IP Ether time 00 192.168.068.017 0010:6076:8351 19 01 192.168.068.016 0021:7093:d178 22
The printout contains the IP and Ethernet address of the station
with which the ARP packet was exchanged and the remaining duration of
validity of this record, see (A)RP ttl.
An example of a printout of a locked table ARP :
ARP cache: IP Ether time 00 192.168.068.017 0010:6076:8351 0 01 192.168.068.016 0021:7093:d178 0
| Note | |
|---|---|
For locking table ARP Setr version 10.0.94.0 and higher is required. |
The continuation of EPe 0 menu by the last item:
| parame(t)ers | — setting of other parameters |
Type t Enter
INTERNET PROTOCOL GATEWAY:
M-IP-M:
(A)rt:0; write (E)nable:ON
(b)ase:00000000 MAS(K):00000000 s(h)ift:0000 ->set Security off!
(r)epeats:0000 Sec(u)rity:ON (t)imeout:0 (p)roxy timeout:0s
(f)rag size:400bytes (g)lue (append) up to:0packets
IP-M-IP:
(I)PArt:0
b(a)se:00000000 (m)ask:00000000
IP(F)rag. size:552
MAS:
(s)Art:0; write (e)nable:ON
(B)ase:00000000 (M)ask:00000000
BEWARE! IF YOU CHANGE CONTENT OF THE ART TABLE,
YOU SHOULD RESTART (INIT) THIS PROTOCOL!
(P)inger (S)tatus
Firewall (T)ype:0000 A(d)dress:00000000 Mas(k):00000000
Unix Time:
e(n)able:OFF per(i)od:0s
time (H)ost:00000000
(q)uit
>>Before the gateway description let see the commands (P)inger and (S)tatus :
ICMP ping: (t)arget:00000000h 0.0.0.0 pe(r)iod:1000ms p(a)ttern:DEDAh si(z)e:100 (s)tart r(e)port sto(p) (q)uit >>
Using the (s)tart command you can ping the ICMP
packet to the IP address (t)arget and in this way test the
communication.
| (t)arget: C0A80001h 192.168.0.1 | — the target IP address |
| pe(r)iod: 5000 | — the repeat period [ms] |
| p(a)ttern: DEDAh | — the sended hexa characters |
| si(z)e: 100 | — the whole length of packet sended |
| (s)tart | — start packet sending |
| r(e)port | — the sending and receiving report |
| sto(p) | — stop packet sending |
IP frames multicast
The Firewall menu allows multicast IP frames to be processed:
Firewall (T)ype:0000 A(d)dress:00000000 Mas(k):00000000
| (T)ype |
|
In mode 3 - mcast some received IP frames are
transmitted further as MORSE broadcast packets. These IP frames are
chosen according to their address IP dest using
parameters A(d)dress and Mas(k), for
example:
A(d)dress:C0A821FF Mas(k):FFFFFFFF
or
A(d)dress:000021FF Mas(k):0000FFFF
Terminal CUs must have the set parameter (T)ype:3,
parameters A(d)dress and Mas(k) are empty; see
the example in the manual How to
guide to MORSE 3. All CUs on the MORSE route must have the
correctly set parameters in the Broadcast menu.
The statements (S)tatus group are used for service
purposes.
The Unix Time group enables getting time from the
Unix machine.
We can show the related menus again for better orientation including Art tables.
Etp: (i)p adr:C0A80009h (g)ateway adr:00000000h (n)et mask:FFFFFF00h (G):0000 AR(P) parameters parame(t)ers ...
INTERNET PROTOCOL GATEWAY:
M-IP-M:
(A)rt:0; write (E)nable:ON
(b)ase:00000000 MAS(K):00000000 s(h)ift:0000 ->set Security off!
(r)epeats:0000 Sec(u)rity:ON (t)imeout:0 (p)roxy timeout:0s
(f)rag size:400bytes (g)lue (append) up to:0packets
IP-M-IP:
(I)PArt:0
b(a)se:00000000 (m)ask:00000000
IP(F)rag. size:552
MAS:
(s)Art:0; write (e)nable:ON
(B)ase:00000000 (M)ask:00000000
BEWARE! IF YOU CHANGE CONTENT OF THE ART TABLE,
YOU SHOULD RESTART (INIT) THIS PROTOCOL!
(P)inger (S)tatus
Firewall (T)ype:0000 A(d)dress:00000000 Mas(k):00000000
...ART No 1: items: 3 default gw: C0A80F00 dest: gw: 6990508E C0A80F05 69905091 C0A80F06 69905094 C0A80F07 ART No 2: items: 2 default gw: 693A0000 dest: gw: C0A8050E 6932000E C0A80506 693A000D ART No 3: items: 3 default gw: 00000000 dest: gw: 690F9002 22B8711D 690F9042 22B85024 690F9043 22B80A01
Packet retranslation from the MORSE network through the IP network to the MORSE network again.
Configuration
the Ethernet channel is connected to the node net output
the node is connected to the retranslation output from Ethernet channel
nonzero (1-4) content of (A)rt activates the M-IP-M mode
Processing of the packet:
The packet with MORSE address
TOcomes from the MORSE network.Mask conversion of addresses
The MORSE address
TOis compared with the parameter(b)asein those parts where theMAS(K)has zeroes (in bits). If there is a match the addressIPdestis created by masking.The MORSE address
TOis compared with the parameter(b)asein those parts where theMAS(K)has zeroes (in bits). If there is a match the addressIPdestis created by masking.For bits where there are ones in the
MAS(K)there must be zeroes in the(b)ase.For mask conversion of an address
Sec(u)rity:OFFis required.Conversion of addresses via table Art
If the conditions for mask conversion of an address were not complied with then table
Artis used.In the
(A)rttable pertaining to M-IP-M mode the IPdest address is determined according to the MORSE addressTO.If the
TOaddress isn’t in the table thendefault gwis used from this table.The next direction in the IP network is determined according to destination IP address with help of parameters from the first part of menu
Etp. If the condition(IPdest & (n)et mask) = ((i)p adr & (n)et mask)is fulfilled then the packet is sent to the destination IP address. If the condition is not fulfilled then the packet is sent to the address
(g)ateway adr.The MORSE packet is completed with the IP header and is sent to the IP network. The following parameters can be used:
(r)epeats: 0005 — max. number of repeats when sending through IP
(t)imeout: 100 — timeout (ms) for waiting for ACK in IP
(p)roxy timeout: 0 s 10 and more – the interval of sending identification packets through the proxy server
0 – off
(f)rag size: 400 bytes — minimal adjustable value is 200, recommended 400 to 1400 – max. length of packets for IP, longer ones will be divided
(g)lue (append) up to: 0 packets — in progress, max. number of joinable packets, put in the value 0
The packets travels according to IP network rules.
Upon output from the IP network the IP header is removed and the packet is handed to the MORSE network and continues on its way according to MORSE routing.
![[Note]](/images/radost/images/icons/note.png)
Note By using the
write(E)nable:OFFparameter we can disable the automatically fulfilling of Art table, which comes up in some modes.
Conversion of addresses
using a mask with
Sec(u)rity:OFF permits an unlimited number of addresses to be
used and makes better use of the transmission capacity of the IP
channel. Security, if required, needs to be implemented on different
communication layers. Fragmentation is not available here. The
recommended value is (f)rag size: 1400 bytes, which is
the max. size of transmitted packet.
Conversion of addresses using table
Art is limited to approx. 100 addresses. Only a small
portion of the transmission capacity of the IP channel is used. On
selecting Sec(u)rity:ON fragmentation proceeds in parts
according to parameter (f)rag size: 1400 bytes. On
selecting Sec(u)rity:OFF fragmentation is not available.
The recommended value is (f)rag size: 1400 bytes, which
is the max. size of transmitted packet.
Retranslation of packets from the IP network through the MORSE network to IP network again.
Configuration
Eth is connected to the node user output
node is connected to the Eth user output
nonzero (1-4) content of
(I)PArtactivates the IP-M-IP mode
Processing of the packet runs in these steps:
The packet with destination address
IPdestcomes from the IP network to my addressMyIP.The MORSE address is found in next steps:
Art
The Morse address
gwis found in table(I)PArtaccording to theIPdestaddress, which signifies the destination address in the MORSE network.Mask
If the
IPdestis not found in the left column of(I)PArt, then comparison of the addresses(b)asefrom IP-M-IP menu andIPdestis made by application of the bit-inverted value of(m)ask, thus((b)ase & ~(m)ask) = (IPdest & ~(m)ask)If this condition is fulfilled, then the destination MORSE address
Morsedstis determined as my Morse addressMyMorsemasked by the bit-inverted value(m)askcompleted byIPdstmasked by(m)askthusMorsedst = (MyMorse & ~(m)ask) | (IPdst & (m)ask)Example 1:
MyIP 192.168.15.128 C0 A8 0F 80 IPdst 192.168.15.04 C0 A8 0F 04 (m)ask 0xFF 00 00 00 FF condition fulfilled MyMorse 69 0F 90 43 Morsedst >> 69 0F 90 04Default gw
If the condition is not fulfilled or if
(m)ask = 00000000, then the addressdefault gwis used from(I)PArttable.Example 2:
MyIP 192.168.15.128 C0 A8 0F 80 IPdst 192.168.05.06 C0 A8 05 06 (m)ask 0xFF 00 00 00 FF condition is not fulfilled ART1 default gw 69 3A 00 00 Morsedst >> 69 3A 00 00IP packet is completed by the MORSE header and is sent in MORSE network to the
destinationaddress.The packet goes through the network according to MORSE routing.
At the output point from the MORSE network in the CU, which has Morse address
Morsedstand simultaneously IP addressCUadrIPthe MORSE head is removed.The next routing in the IP network is defined according to the destination IP address with use of the parameters from the first part of menu
Etp. If the condition( IPdest & (n)et mask ) = ( CUadrIP & (n)et mask )is fulfilled then the packet is sent to the destination IP address.
Example 3:
CUadrIP C0 A8 0F 20 packet's IPdst C0 A8 0F 04 (n)et mask FF FF FF 00 condition fulfilled packet send to IP C0 A8 0F 04If the condition is not fulfilled, then the packet is sent to the Ethernet address which has the equipment with IP address
(g)ateway adr.Example 4:
CUadrIP C0 A8 0F 20 packet's IPdst C0 A8 10 04 (n)et mask FF FF FF 00 condition is not fulfilled (g)ateway adr C0 A8 0F 00 packet send to IP C0 A8 0F 00
It is used for packet sending to and from the MORSE network through the MORSE Application Server into the IP network.
Configuration
the Ethernet channel is connected to the node user output
the node is connected to the Ethernet user output
parameter
(s)Artdifferent then zero oroff(from fw 10.0.18.0) activates the MAS mode
The packet sending from MORSE network through MAS to the IP network.
The packet with destination MORSE address
MasMorse, which belongs to the application server, comes from the MORSE network.Check as to whether it fulfils the condition
(MasMorse & ~(M)ask) = ((B)ase & ~(M)ask)If yes then the packet is sent to the Morse Application Server, if not then it is sent to
IP_M_IP. The next condition for MAppS is the user packet type (user_data 0x09, prot_data 0x0A), not the retranslation.In the table
(s)Artbelonging to Morse App. Server the itemgwis found according to the destination MORSE address and then it is processed as follows:The lower part of
gwis used as the lower part of resulting IP address of length 14 bits from the right. The 15th and 16th bit are used for internal purposes. The upper part of the IP address (18 bits) is completed from its own CU IP address.The higher part of
gw(as a rule22B8 hex) is converted into (dec), here 8888 , and becomes a UDP port number.
The packet is sent to the IP address and UDP port created in this way.
So the packet coming from MORSE network to the MAS (Morse Appl. Server) contains MORSE addresses
srcanddst. After processing in MAS it contains the IP address, UDP port number andsrcMORSE addr.![[Note]](/images/radost/images/icons/note.png)
Note By using the
write(e)nable:OFFparameter we can disable the automatically fulfilling of Art table, which comes up in some modes.
The packet sending from IP application through MAS to the MORSE network
The packet with destination MORSE address
MorseDstcomes from the application (daemon) running on the addressIPAddrand portAppPort.The items
AppPortandIPAddrare assembled to create thegw, which is found in the Art table. The 14 LSB from IPAddr creates the right part ofgw, the bit No 15 is 1 for broadcast, the bit No 16 is 0 for manually created Art, the bits No 17 to 32 are borrowed fromAppPort.The created item
gwis used to found the respective itemdestin the Art table. The founded itemdestbecomes thesourceaddress in the MORSE packet, which is sent into MORSE network.So if the application sends the report back through MAS to the MORSE network, then it contains the IP address of the application, UDP port number and
dstMORSE address. After processing in MAS it contains MORSE addressessrcanddst.
The default MORSE address for IP —> MORSE direction.
Works in sw 570 and later.
The packet sent from the Application via MAS to the MORSE network in some cases has not assigned the port number. It is possible to define the default MORSE address for the Application, which is found in the Art table in three steps:
After unseccesful searching in the
gwcollumn in Art tableis found the address
00000000in thedestcollumn. The itemgwbelongs to this address, e.g.22B86420, where22B8is the choosen standard port number and6420is the low part of Application IP address. This pair00000000 22B86420must be located on the end of Art table, so the pair mentioned in next point e.g.:744901BB 22B86420appears above it.This item
22B86420is then found in thegwcollumn and the itemdest 744901BBbelonging to it becomes the MORSE addresssourcein the sent packet.
Art table choice in MAS mode
In older fw the Art table is selected by writing number 1 to 4
into parameter (s)Art:, the value 0 switches off the MAS
mode.
From fw 10.0.18.0 choose from the menu:
sArt (f) off ...MAS mode turned off (1) ART1 ...Art1 (2) ART2 ...Art2 (3) ART3 ...Art3 (4) ART4 ...Art4 (9) ART9 ...MRouter writes into file instead of the Art table (s) single address ...only one IP address connected, see bellow
Single address mode is determined for the communication with only one IP address which is greater by one than the address written in menu EPe. The communication runs between ports 8888dec and 8888dec. Configuration example:
Internet Protocol: Eid| ip address | net mask | gw | (0) C0A801E7 192.168.1.231 FFFFFF00 255.255.255.0 00000000 0.0.0.0 MAS: (s)Art:single address; write (e)nable:ON (B)ase:690F5600 (M)ask:00000000
PC having address 192.168.1.232 is connected by the command:
setr.exe -pIP192.168.1.231 -pw690f5600 -pm8888
The choice single address is suitable for communication PC-CU using the protocol SLIP.
The format of the frames of MAS and UDP is described in the article Format of UDP datagram IPGW for Morse